For those who enjoy Counter-Strike in particular, the launch of Counter-Strike 2 has been an important event in the gaming industry. With CS2, which takes the place of Counter-Strike: Global Offensive, a game that dominated the competitive first-person shooter arena for more than ten years, many improvements are anticipated. CS:GO’s smooth gunplay, intricate strategy, and wide audience appeal helped it achieve its zenith, but CS2 must elevate the franchise to new heights.The new game brings a host of technological and gameplay innovations, making the CSGO vs. CS2 debate a hot topic among players and esports enthusiasts alike. In this article, we’ll take a look into all the CS2 changes, examining how it stacks up against CSGO, including its impact on CS2 esports, its system requirements, and more.
Source 2 Engine: Visual and Performance Enhancements
The most striking difference between CSGO and CS2 lies in the adoption of the Source 2 engine. This engine, already familiar to players from Valve’s other titles, offers significant upgrades in terms of graphics and game physics.
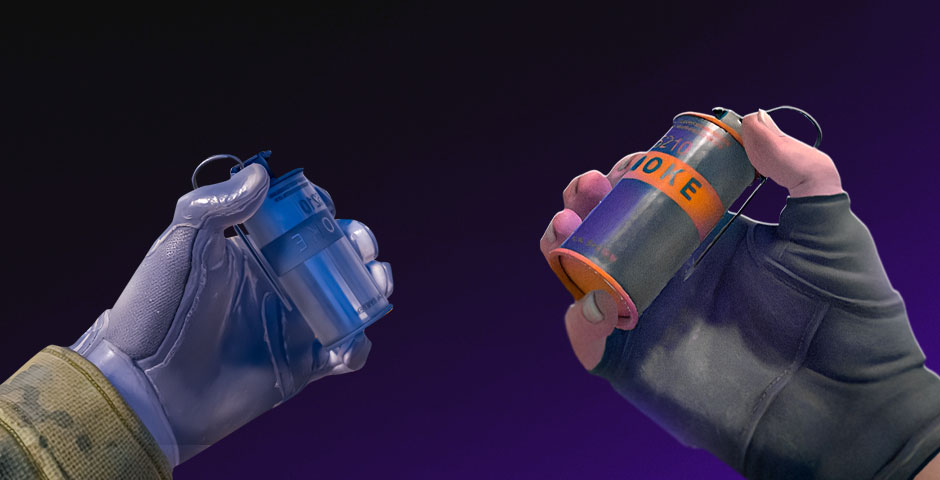
Volumetric Smokes and Enhanced Environments
Volumetric smoke grenades are one of the most notable additions to CS2. Smokes were static clouds in CS:GO, and players frequently used exact setups to carry out plans around them. But in CS2, smokes act in a dynamic way. They occupy space, react instantly to changes in lighting, and interact with explosives and gunfire. A well-placed grenade can momentarily remove some smoke, opening the door for split-second maneuvers that infuse every game with an extra degree of tactical intricacy.
The environment itself has become more interactive and detailed. CS2 maps now feature higher levels of texture detail, more realistic reflections, and shadows that enhance immersion. Source 2 allows for better optimization of resources, but this also means that CS2 requires more hardware power to run efficiently compared to CSGO.

Performance and System Requirements: Can You Still Play CS:GO After CS2?
CS:GO’s Source engine was extremely efficient, allowing the game to run smoothly on low-spec machines. This accessibility made CS:GO one of the most popular games in regions where high-end gaming hardware was scarce. The game’s low system requirements contributed to its widespread success, particularly in the esports scene.
With CS2, Valve has updated the game’s system requirements to meet modern standards. While CS2 isn’t excessively demanding compared to other contemporary games, it does require a more powerful setup than CS:GO. Minimum requirements include a 4-thread Intel Core i5 processor, 8 GB of RAM, and a DirectX 11-compatible GPU with at least 1 GB of VRAM. This shift is significant for players still running older hardware, as they may struggle to achieve competitive frame rates.

Tick Rate vs. Sub-Tick System: A Technical Leap
One of the most technical, yet essential, differences between CSGO vs. CS2 is the way the games handle server communication. CSGO utilized tick rates, specifically 64-tick and 128-tick servers, to process player inputs. While 128-tick servers were preferred by competitive players for their responsiveness, CS2 introduces a sub-tick system that makes tick rates irrelevant.
How Sub-Tick Works
In CS2, the sub-tick system registers every player’s input (whether it’s shooting, moving, or throwing utility) with perfect precision, regardless of the server’s tick rate. This means that actions are recorded more accurately between server updates, offering a more seamless and responsive experience. This shift is particularly impactful in CS2 esports, where split-second decisions and timing can be the difference between winning or losing a round. Sub-tick could very well redefine the standards for competitive gameplay, giving players a more fluid and responsive experience than ever before.
Read how Valve enhanced Counter-Strike 2 tick rates with a sub-tick system. Discover its in-game mechanics in our article!
Matchmaking and Competitive Play: The New MR12 Format
The MR12 format, which differs greatly from the MR15 format used in CS:GO, is a major addition to CS2’s competitive mode. Instead of playing 15 rounds every half, teams play a maximum of 12 rounds under the MR12 system. The winner is the first team to win 13 rounds. This alteration quickens gameplay without compromising the game’s depth or strategic components, enabling more matches to be played in less time.
A new round format – Is MR12 Better Than CS:GO’s MR15? We’ll attempt to explain the differences between these two formats.
Revamped Overtime System
CS2 has also seen changes related to time. In the case that the game is tied (12–12), each team will play three rounds of overtime. The winner is the team that wins four rounds in a row; this allows tied games to be settled quickly and thrillingly. This change streamlines the CS:GO experience for both players and spectators by lessening the grind of extended overtimes.

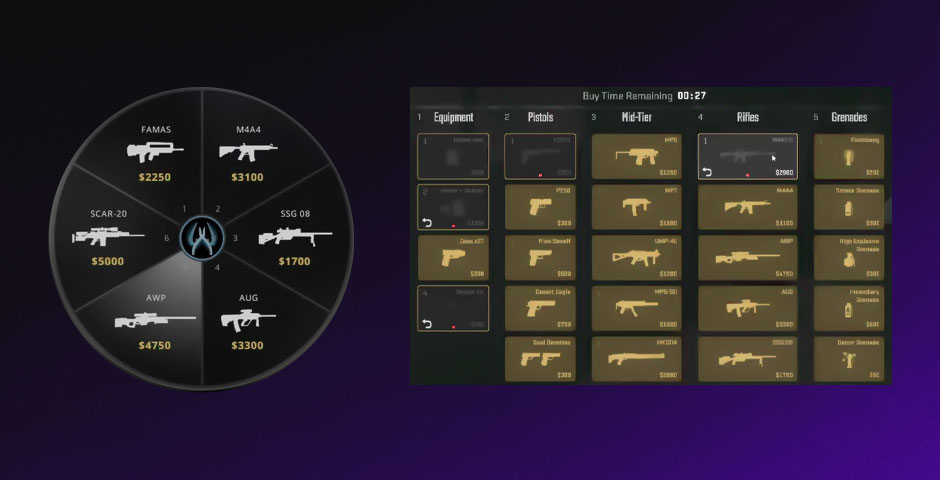
The New Buy Menu and HUD
CS2 introduces a reimagined buy menu that has a more intuitive layout compared to CSGO. Instead of the circular buy menu from CS:GO, which required players to remember where specific weapons were located, CS2’s buy menu displays all items at once. This Valorant-like buy system makes purchasing decisions quicker and more accessible, particularly for new players.
Additionally, the Heads-Up Display (HUD) in CS2 has been redesigned. Health, armor, and money are now displayed at the bottom center of the screen, providing a more centralized view of essential information. This new layout is not only more modern but also offers better clarity, especially in the fast-paced moments of a match.
Weapons and Utility: Changes in CS2
CS2 has seen several changes to weapons and utility items, enhancing gameplay in both casual and competitive settings. The AK-47, M4A1-S, and AWP—staples of CS:GO—are still central to the competitive meta, but their sounds, firing mechanics, and overall feel have been subtly tweaked for greater immersion.
Discover the ultimate CS2 weapons tier list for 2024, outlining the top picks and strategies dominating the current meta.
New Inspect Grenades Feature
One small but significant change in CS2 is the ability to inspect your grenades. This allows players to cycle through their grenades to see exactly what utility they have on hand, eliminating the need for guesswork in clutch moments. This feature, while simple, is a valuable addition that improves decision-making during high-pressure rounds.

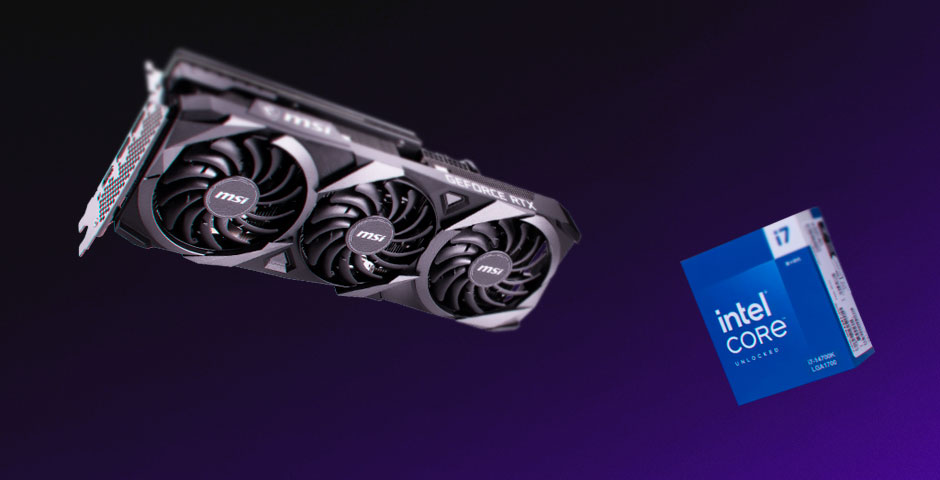
CPU and GPU Optimization: Better Usage in CS2
One of the long-standing issues with CS:GO was its CPU-bound performance. The game often failed to fully utilize modern CPUs and GPUs, leading to performance bottlenecks, particularly on higher-end systems. CS2, however, appears to be much better optimized for modern hardware, using both CPU and GPU resources more effectively.
CS2’s improved GPU utilization ensures that players with high-end graphics cards will see more consistent performance, while multicore CPU support leads to better frame rates in general. This optimization reduces the stutters and freezing issues that were often reported in CS:GO, particularly in intense firefights or large maps.
Dominate the game with the best CPU for CS2. Maximize FPS, minimize lag – experience precision and speed like never before.

Final Thoughts: CSGO vs. CS2
It’s evident from the CSGO vs. CS2 battle that CS2 offers a ton of new features and enhancements that usher in a new era for the Counter-Strike series. With improvements to graphics made possible by the Source 2 engine and a revolutionary sub-tick system, Counter-Strike 2 is more than just an upgrade—it’s a reimagining of what Counter-Strike can be.
While CS:GO will always be remembered as one of the greatest first-person shooters of all time, CS2 takes everything that made its predecessor great and builds on it with modern technology and refined mechanics. With this updated version of the game, you can expect a more dynamic and engaging experience for years to come, regardless of your skill level. This is especially true for professional players competing in CS2 esports.

































![kyousuke CS2 Settings: Full Guide [2025]](https://skin.club/community/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Main-x-Name.jpg.webp)






